Treatment for Sleep Apnea and Intense Snoring
Discover how we can help you treat obstructive sleep apnea and reduce snoring to improve your quality of life.

What is sleep apnea and why is its treatment important?
Symptoms of sleep apnea and snoring
- Loud, choppy snoring
- Apneas (respiratory pauses)
- Hypopneas (softer apneas)
- Dry mouth when you wake up
- Need to drink water at night
- Increased frequency of going to the bathroom during sleep
- Drowsiness during the day, in the absence of stimuli that keeps us alert
- Restless sleep
- Multiple awakenings
- Feeling tired or unrefreshing sleep when you wake up
- Neuropsychological alterations: decreased concentration, memory and libido.
- Morning headaches
- Fall in oxyhemoglobin saturation (decrease in blood oxygen)
- Diastolic hypertension (high minimum blood pressure)
- Heart rhythm disturbances
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Cardiac hypertrophy
These symptoms, particularly severe snoring and daytime sleepiness, should not be ignored. If they occur frequently (every day), it is essential to seek medical attention to confirm a diagnosis and begin treatment.
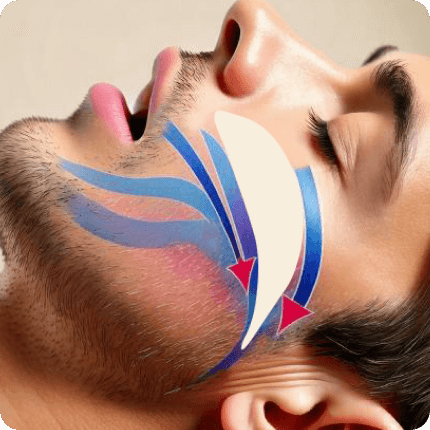

Are you looking for solutions to stop snoring and improve sleep quality?
Snoring is not only annoying for sufferers and their companions during sleep, but it can also be an indicator of more serious problems such as sleep apnea. If you’re wondering how to stop snoring, it’s essential to get a proper diagnosis to determine if your snoring is related to an underlying health problem. At the Estivill Sleep Clinic, we are specialists in diagnosing and treating sleep apnea and snoring, we evaluate your situation and offer you personalized treatments to stop snoring, ranging from lifestyle changes to the use of devices to stop snoring. improve breathing: CPAP (Continuous Positive Air Pressure), MAD (Mandibular Advancement Device), scientifically proven solutions that improve quality of life and night’s rest.
Do you want to improve your rest?
Contact our snoring and sleep apnea specialists for a personalized evaluation.
Make an appointment!
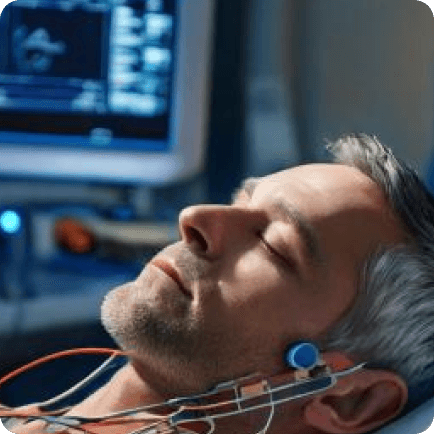
Diagnosis of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome
Do you suspect you might have sleep apnea?
To determine the most appropriate treatment, an accurate diagnosis is necessary.
At our clinic, we perform advanced testing, such as comprehensive polysomnography (overnight sleep studies) to identify the type and severity of apnea. Only through a proper diagnosis can we begin the best treatment for sleep apnea.
We can also perform these complete polysomnography studies on an outpatient basis, at the patient’s home.
Sleep studies record sleep behavior, including:
- Information about sleep quality (shallow, deep, and REM sleep)
- Information on microawakenings caused by apneas
- Number of total apneas and hypopneas (we determine the number of apneas per hour, which indicates the severity of the process)
- Degree of hypoxia (lack of oxygen)
- Changes in heart rhythm
Polysomnography helps us classify the severity of the disorder and guide the most appropriate treatment for sleep apnea.
If snoring is affecting you or your partner, and you feel tired and sleepy during the day, it’s time for a complete evaluation.
Click here for more information on diagnosing snoring and sleep apnea

Causes and aggravating factors in snoring and sleep apnea
Several factors can influence the severity of sleep apnea and snoring symptoms. Considering them is essential for a complete diagnosis and effective intervention. Among these factors are:
1/ Excess body weight (fat accumulates in the abdominal area and neck)
2/ Genetic characteristics
- A short and wide neck. When we relax when we fall asleep, the inner part of the neck closes and causes snoring and apneas.
- Retromicrognathia (small, retracted jaw that reduces airway space). This characteristic of the face causes snoring to occur when we sleep on our back due to the closure of the air passage (pharyngeal collapse). In these cases, sleeping on your back causes the jaw to fall backwards, closing the air passage. Changing position (do not sleep on your back) using a small pillow placed on your back (Bumper belt)
3/ Other situations
- Structural craniofacial alterations
- Neurological and muscular disorders,
- Special attention to people with Down Syndrome who usually present significant apneas due to their genetic characteristics (short and wide neck, large tongue and muscle hypotonia, low muscle tone)
- Smoking can make these situations worse.
- During menopause there is an increase in fluid retention and can cause a slight weight gain. Consequently, snoring and in some cases also apnea appear.
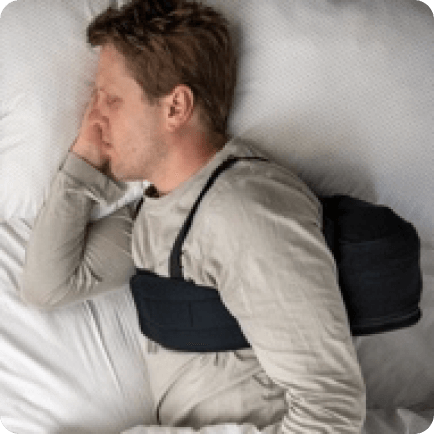

Bumper Belt
Treatments for gnawing and sleep apnea
Treatment for sleep apnea and snoring depends on the cause. Diagnosis is key to reducing serious risks and improving our health, using the most appropriate treatments.
If you suffer from snoring and suspect you may have sleep apnea, it is important to seek treatment. At the Estivill Sleep Clinic, we offer you personalized, scientifically validated and effective solutions to treat both snoring and obstructive sleep apnea.
These treatments include:
CPAP devices for apnea

CPAP (Continuous Positive Air Pressure)
One of the most effective sleep apnea treatments is CPAP (Continuous Positive Air Pressure), commonly called an apnea machine. It is a small device similar to a fan (compressor) that collects air from the environment and sends it to our nose through a mask and opens the passage of air that is obstructed.
The most important thing is to determine, through a sleep study, the amount of air necessary to achieve good tolerance and make it comfortable for the patient.
Our specialists will help you choose the best CPAP most suitable for you (through mutual insurance, social security, or buy it at the best price).
MAD (Mandibular Advancement Device)

MAD (Mandible Advancement Device)
The Mandibular Advancement Device (MAD) is an intraoral appliance that is used when the cause is retro-micrognathia (small, backward-moving lower jaw). It is placed in the mouth overnight and works by gently advancing the lower jaw to keep the airways open.
It should be recommended after a nocturnal sleep study (polymonography) and adapted by an expert dentist specialized in sleep. From the clinic we will refer you to the best specialist to adapt the DAM.
Corrective surgery
In some cases and depending on the cause that causes snoring or apneas, it is highly recommended to consult with an Otorhinolaryngologist. (ENT)
Children who snore: In the case of children with significant adenoid hypertrophy (large tonsils and turbinates), which cause breathing collapse when sleeping, surgical treatment is totally indicated. Removing these tissues will completely solve the problem.
In adults: It may be useful if there is hypertrophy of the adenoids or uvula (bell ring). These are rare cases. Removal of the uvula and part of the palate is ineffective (uvulo-palato-pharyngoplasty).
In children and adults with a severe mandibular malformation, the jaw is advanced (surgical correction). It can be very effective and necessary when conventional means (CPAP or DAM) are insufficient. They are rare cases
Solutions to stop snoring

In addition to CPAP, DAM or Bumper belt as suitable treatments for apnea and snoring, there are combined therapies that help stop snoring.
Modifying lifestyle, an adequate diet, losing weight or reducing alcohol and tobacco consumption can also improve snoring, thus achieving a comprehensive and personalized approach to treatment.
Treatment for snoring and apnea is essential to improve quality of life, reduce associated risks and avoid more serious complications, such as hypertension, stroke and heart disease.
At the Estivill Sleep Clinic, we offer advanced and personalized solutions to treat this disorder, helping you regain restful sleep and improve your general health.
Snoring and sleep apnea: When to seek treatment?
If you experience symptoms such as severe snoring and excessive daytime sleepiness, it is essential to seek diagnosis and treatment for sleep apnea. At the Estivill Sleep Clinic, we offer you a comprehensive and personalized medical approach, guiding you towards a solution that adapts to your needs, improves your rest and helps you regain restful sleep.
Contact us to improve your sleep and health
Don’t let sleep apnea or snoring interfere with your quality of life. We are specialists in sleep apnea treatments and solutions to stop snoring that really work. Contact us for a complete evaluation and find out how you can stop snoring and enjoy a restful night’s sleep.
FAQ’s
Frequently Asked Questions about Sleep Apnea, Snoring and Treatments
What solutions exist to stop snoring?
Solutions to stop snoring vary depending on the cause of snoring. They may include lifestyle changes, anti-snoring devices (AMDs), surgery, or the use of a CPAP device for cases related to sleep apnea.
What is obstructive sleep apnea and how is it treated?
What solutions exist to stop snoring?
Solutions to stop snoring vary depending on the cause of snoring. They may include lifestyle changes, anti-snoring devices (AMDs), surgery, or the use of a CPAP device for cases related to sleep apnea.
What treatments are available for loud snoring?
Treatment for loud snoring depends on the cause. It can include everything from DAM anti-snoring devices, Bumper belt, to the use of CPAP in cases associated with obstructive sleep apnea.
